Varicose Veins Aesthetic Treatments


Superficial vein dilatations that become visible on the skin, whether due to varicose veins or not, are common. These thin capillaries are called “telangiectasias”. Telangiectasias are thin, tortuous and often branching, purple or red veins that are close to the surface of the skin. Although they are not a medical problem, individuals may be disturbed by the appearance of these veins. This discomfort sometimes may cause the patients to limit their clothing choices and be dissatisfied with themselves. In such cases, we may apply the injection treatment method called ‘sclerotherapy’ or superficial laser or radiofrequency ablation methods for capillaries in order to reduce and sometimes to eliminate the disturbing appearance of these superficial veins.
Sclerotherapy

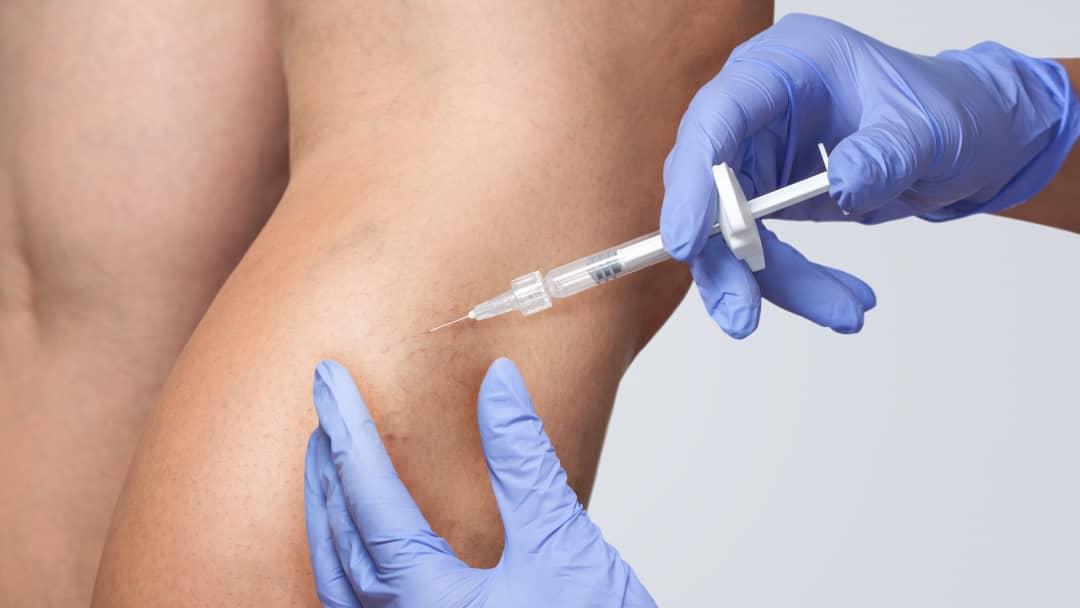
Sclerotherapy is a procedure commonly used for the treatment of superficial veins that have become visible (spider veins, superficial capillaries or larger venous dilatations). It is a treatment method in which a special drug called “sclerosing agent” is injected into the visible veins with an injector, aiming to make the veins disappear.
This drug damages the inner surface of the vein and causes the vein to close and disappear over time by sticking or narrowing the vein wall. It is generally known as “foam treatment” among the public (not wrong but lacking information), but foam treatment is actually a subheading of sclerotherapy. If the drug used is applied alone, it is called “liquid sclerotherapy“, and if it is applied by mixing it with air, it is called “foam sclerotherapy“.
Sclerotherapy treatment is often desired by patients for cosmetic purposes. It is especially effective in treatment of spider veins or small varicose veins that have an aesthetically disturbing appearance for patients. However, in some cases, it can also be used in the treatment of larger veins and is said to have an effect in symptom regression.
The sclerotherapy procedure does not require local anaesthesia and can be performed in outpatient clinics. Since a very fine needle is used during the procedure (the same needle is used for face for botox applications), there is usually none or minimal discomfort. It is possible to treat more than one vein in one session. However, since superficial vein dilatations can be common in the legs, repeated sessions may be required. Temporary side effects such as mild swelling, redness or bruising may be experienced in the post-sclerotherapy period. The recovery process is usually rapid, and most patients can return to daily activities immediately. However, it is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations, especially wearing compression stockings or avoiding heavy exercise. If a larger varicosity excision was performed, the stitches on the small incisions are recommended to be removed after 10 days.
Although sclerotherapy is generally an effective and safe treatment option, it may not be suitable for everyone. It is important to inform your doctor before sclerotherapy, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding or if you have a medical condition such as deep venous thrombosis. It is also important to know that treatment results may vary from person to person and even from vein to vein in the same person.

Superficial Laser Ablation (Exo-laser)
Laser applications in capillary vessel treatment are effective choices that are widely used, especially in treatment of small and superficial veins. Different lasers such as IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) or Nd:YAG can be applied for this purpose. This treatment is usually performed by applying laser light directly to the skin surface. This laser light targets pigments such as haemoglobin and melanin in the capillaries under the skin. The absorption of the laser in the targeted veins increases the temperature inside the vein, causing the vein to coagulate (clot) and disappear. This process results with the vein being absorbed by the body over time and becoming invisible. When applied correctly, laser capillary treatment usually provides effective results and, in most cases, there is visible improvement. Laser treatment causes few side effects, mostly limited to temporary side effects such as mild redness or swelling. The decrease or, in some cases, disappearance of the unwanted image is observed over time. However, laser capillary treatment is not suitable for every vein and treatment results may vary from person to person. In cases of widespread vascular dilatation, sclerotherapy and device treatments such as laser or RF may be used together depending on the vessel diameter. It is important to consult a Cardiovascular Surgery Doctor before treatment.
Superficial Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation (Exo-RF)
Radiofrequency needle telangiectasis treatment is a method used in the treatment of telangiectasias (thin capillaries). In this treatment method, radiofrequency energy is delivered into the vein through a thin needle and heats and damages the vein wall, causing the vein to close and disappear. The procedure is usually quick, and minimal pain may be felt during the procedure, depending on the energy given. The recovery process is usually quick, and the patients can return to their daily activities immediately. It is important to follow your doctor’s recommendations. Every patient is different, and it should be kept in mind that the effectiveness of the treatment may vary depending on individual factors.
Cryo Laser Cryo Sclerotherapy (CLaCs)
This is an acronym used to describe a specific procedure that is used to treat telangiectasis. This term refers to a treatment protocol that combines venous mapping followed by cryotherapy (cold application), laser therapy, and sclerotherapy. In this treatment protocol, four different methods are used together to treat telangiectasias:
- Venous mapping: Special devices that show superficial veins are used to mark the superficial veins and the deeper nonvisible veins that feed them.
- Cryotherapy: The aim of cryotherapy is to prevent pain and cause the vein to spasm.
- Laser therapy: With low-dose laser therapy, the blood in the vein is heated and the vein wall is destroyed, initiating the closure of the telangiectasis.
- Sclerotherapy: With sclerotherapy, a sclerosing substance is injected into the vein, destroying the inner surface of the vein and closing the vein.